1 Introduction
This article refers to the address: http://
Since the 1970s, Fanger put forward the thermal comfort evaluation index-PMV index based on the human body thermal comfort equation and the ASHRAE seven-point scale. The research on thermal comfort in the world has entered a new era, especially on the basis of this standard. Control studies conducted have provided people with a more comfortable indoor environment. However, with the improvement of living standards, people have higher requirements for indoor environment, and with the wide-scale promotion of energy conservation, we are required to not only meet people's comfort but also pay attention to energy conservation.
The indoor heat and humidity environment affecting the human body is composed of a plurality of elements. For the environment side, in addition to the temperature, humidity and flow rate of the air, there is an average radiation temperature of the environment to the human body; for the human body side, there is a metabolic production of the human body. Heat and clothing thermal resistance [3]. The feeling of cold and heat in the environment is the result of the joint effects of these six factors on the human body [4]. As far as the four environmental variables are concerned, the degree of influence on human comfort is different, and the degree of influence on system energy consumption is also different. Therefore, it is possible to adjust the combination of various parameters to minimize the energy consumption of the system under the premise of comfort [4]. For example, in the summer, when other factors are constant, the combination of temperature and wind speed is adjusted. Since airflow is one of the cheapest air conditioners, if the wind speed is increased while increasing the indoor air temperature, it is not only conducive to energy saving but also greatly improves indoor air quality. This is because the indoor air temperature is increased, the temperature difference between the indoor and outdoor air becomes smaller, the heat transfer amount through the building envelope structure is small, and the load of the air conditioning system is correspondingly reduced. Under normal circumstances, for every 1 °C decrease in indoor and outdoor temperature difference, the heat transfer through the envelope structure will decrease by 3%-10%; in winter, increase the indoor wall average radiant temperature should reduce the indoor air temperature value through the maintenance structure. The amount of heat lost to the outside world is also reduced. The literature [1] shows that the low-temperature floor radiant heating system can meet the thermal comfort requirements of the human body more than the convection radiant heating system, and the energy saving rate is higher. Therefore, the comfort control has more flexibility than the traditional temperature control, which can achieve the harmony of comfort and energy saving.
2. Traditional thermal comfort control method
2.1 Indirect control of thermal comfort indicators
The traditional thermal comfort control mainly includes the indirect control mode and direct control mode of the thermal comfort index. The literature [7] shows that the indirect control mode of the so-called thermal comfort index is to determine the set value of each environmental variable in real time according to the PMV index. In this control mode, the thermal comfort indicator is not a direct controlled parameter, but an environmental variable is selected as a directly controlled parameter. Here, the PMV indicator is only a criterion for judging. The PMV value is calculated in real time or the PMV value is measured by the PMV smart comfort sensor to determine whether it is within the comfort range. If not, adjust the corresponding actuator to make the PMV value. In the comfort zone.
The combination of wind speed and temperature is the best choice for thermal comfort index control, and different combinations have different control methods. There are two common situations in the indirect control mode of thermal comfort indicators: (1) determining the set value of air temperature according to indoor wind speed, average radiant temperature and air humidity; (2) according to indoor air temperature, average radiant temperature and air Humidity determines the set value of the wind speed. The control principle of these two indirect control modes is shown in Figure 1.
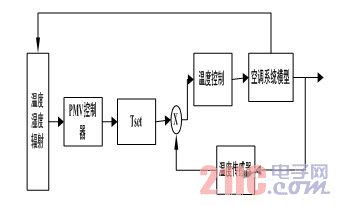
Figure 1 Indirect thermal comfort indicator control with temperature as the directly controlled parameter
Compared with the temperature-only control system, there are the following differences: (1) The set value of the temperature is determined in real time by the PMV controller. On the surface, the system is still a simple temperature setting control, but the temperature value is set to consider the effect of other influencing factors on human thermal comfort. (2) The increased PMV controller section must be able to measure other environmental parameters, while also allowing the body's metabolic rate and clothing thermal resistance to be set according to the actual situation.
In order to achieve energy saving of the system, the set value of the temperature can be increased to 28 ° C, and the method of increasing the wind speed and turbulence can be taken to compensate for the increase of the PMV value caused by the temperature rise. Since the airflow itself is an inexpensive air conditioning method, increasing the set value of the indoor air temperature can greatly reduce the energy consumption of the air conditioning system. Among them, the wind speed sensor is unnecessary because it can be considered that there is a corresponding relationship between the speed of the fan and the wind speed. However, it must be noted that the increase in wind speed cannot be unlimited, and it is generally considered that it can be controlled below 1 m/s; and the noise problem caused by the increase in wind speed must also be taken seriously.
Among them, the indirect PMV control with air temperature as the directly controlled parameter has good applicability in the case of the difference between the average radiant temperature and the air temperature and the adjustment of the wind speed, such as trains, long-distance buses and the like. The control system with the wind speed as the directly controlled parameter is applied in the occasion of easy adjustment of the wind speed. Both of these methods not only improve the thermal comfort of the environment, but also achieve a considerable proportion of energy savings. At the same time, the indirect method of using the thermal comfort indicator control can be well combined with the temperature control system common to the original air conditioning system. It is only necessary to add a PMV controller to the original control system, and the thermal comfort index control of the air conditioning system can be easily realized.
2.2 Direct control of thermal comfort indicators
The direct method of thermal comfort index control is to use the thermal comfort index directly as the controlled parameter to control the air conditioning system. The implementation is also achieved by controlling the temperature and wind speed. In the direct control mode of the thermal comfort index, the PMV indicator is not only an evaluation criterion of the system, but the input of the whole system. Through the internal connection between the PMV index and the temperature and the wind speed, when the PMV index changes, the temperature and the wind speed are adjusted. The corresponding actuators make the PMV value within a comfortable range. Correspondingly, in the direct control mode of the thermal comfort index, [7] also has two cases: (1) determining the set value of the air temperature according to the indoor PMV value; (2) determining the set value of the temperature and the wind speed according to the indoor PMV value. . The control principle is shown in Figure 2.
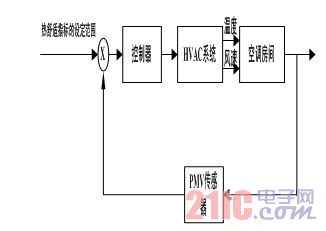
Figure 2 Reset control of temperature and wind speed based on PMV indicator
The second way is to add control of wind speed based on the first method. Compared with the indirect method, the control objective of the direct method is changed from the control of temperature and wind speed to the control of the PMV, which is a measure of human thermal comfort. This is actually an innovation of the existing air conditioning system, not only in theory. The problem is a conceptual change that reflects the new concept of “people-oriented†air-conditioning. The control of the air-conditioning system should not be only the control of some physical quantities such as temperature and wind speed, but also the control of people. Once the comfort of the human body changes, the corresponding actuator should be adjusted to meet the needs of the human body's thermal comfort. Therefore, this method can not only meet the needs of the human body for thermal comfort, but also control the change of comfort with the human body. Variety.
3. Newly emerging thermal comfort control methods
3.1 Intelligent air conditioning system based on fuzzy adaptive controller
Due to the nonlinear characteristics of the PMV index, when it is used to monitor HVAC equipment, it often cannot handle some complicated problems. Therefore, in order to overcome these problems, we introduce an adaptive fuzzy control theory [4]. As shown in Figure 3.
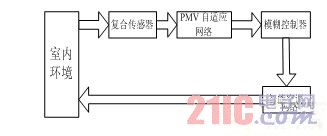
Figure 3 Block diagram of intelligent air conditioning system based on fuzzy adaptive controller
In order to improve the characteristics of the adjustment system, an adaptive network was added based on the original control model, and in order to make the system more stable and reliable, we also modified some control rules. After adding an adaptive network to the original model, you can change the parameter values ​​of the PID integral differential module; therefore, these will depend on the peak of the "step response", which in turn will lead to better stability of the entire system. .
The composite sensor is used to measure four environmental factors: temperature, relative humidity, airflow velocity and average radiant temperature; the collected data is sent to the PMV network, and the PMV network calculates the PMV indicator in real time. This indicator is used as the target of air conditioning control, if PMV If the indicator is within a reasonable range, then the controller can continue to operate without correction. Otherwise, the controller will control the air conditioner to change the airflow speed, airflow direction, etc. to achieve the desired comfortable environment.
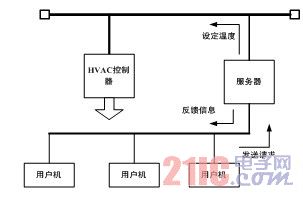
Figure 4 Application example of an emerging method
3.2 Online real-time adjustment according to user needs
Literature [5] summarizes the previous thermal comfort control methods. Whether it is energy saving or the user's thermal feeling, the indoor thermal environment is not optimal. The main reason is that the air conditioning control system does not take people's needs into consideration. Therefore we propose a new air conditioning control method. As shown in Figure 4.
The system is mainly composed of a user machine and a server, and the server is mainly responsible for online communication between the user machine and the air conditioner controller. The intermediate server collects the user requests from the various user machines in the room and determines the temperature values ​​to be set by the LBC, and then sends these commands to the air conditioner controller to adjust the thermal comfort of the room. The user machine transmits the user's request to the air conditioning system just like the terminal, and they also get information about the energy saving of the entire system and some other users' needs from the server.
On the user's input screen are: "slightly warm" and "slightly cool" two request options, "very uncomfortable", "uncomfortable", "a little uncomfortable", "neutral", "a little uncomfortable", " Uncomfortable, "very uncomfortable" seven thermal comfort options, as well as "hot", "warm", "a little warm", "neutral", "a little cool", "cool", "cold" seven hot Feel the option, if the user wants to make the indoor environment a little warmer, you can click "slightly warm", and similarly click "slightly cool", through this input screen users can send their request and the desired thermal feeling to the intermediate server. Of course, after the server collects the user's information, it will use a series of algorithms to determine a series of problems such as how the controller works.
In this system, feedback of various information [5] is considered to be an important part. The purpose of the feedback link is to enable users to accept the system and also to stimulate users to participate in energy conservation.
4, summary
The thermal comfort index control is actually the development of traditional temperature control. The control target of the air conditioning system is changed from the simple indoor air temperature and humidity control to a thermal comfort index that can measure the comprehensive effect of the thermal environment. The control of the air conditioning system changes with the change of human comfort, and under the premise of maintaining the comfort of the human body, the combination of various parameters is adjusted to minimize the energy consumption of the system. Therefore, with comfort control, the unity of comfort and energy saving can be achieved to the greatest extent.
Although foreign countries have been studying comfort control for a long time, and related products related to comfort control have been published, they are still in their infancy in China. With the increasing demand for comfort and energy saving, achieving comfort control is also one of the important trends in HVAC systems. Based on the existing research, it is necessary to conduct further research in the following aspects.
(1) Thermal environment research is one of the basic researches of HVAC. Different races, regions and living habits are not the same for comfort standards. Therefore, based on the actual situation in China, based on the comprehensive foreign research, the thermophysiological theory and experimental research on the characteristics of Chinese race should be carried out.
(2) Due to the multivariate, nonlinear characteristics of PMV indicators and the complexity of HVAC, it is difficult to implement classical control theory in implementation. Therefore, it is necessary to further strengthen the research on various advanced intelligent control strategies in order to better play the superiority of comfort control.
Micro Switch is a tiny contact interval and fast mechanism, with provisions of stroke and force on the contact of Switch action, use the shell cover, the external drive of a switch, because of the switch contact spacing is small, so the micro switch, also called sensitive switch.
Also known as sensitive switch, quick - acting switch.Pressure actuated rapid opening and closing.Used for door switch in anti-theft system.

Micro Switch
Micro Switch,Magnetic Micro Switch,Button Micro Switch,Elevator Micro Switch
Ningbo Best Group Co.,Ltd , http://www.speakerbuzzer.com